Overview
 People think of a bunion as being as a bump on the side of the foot near the big toe. However, bunions go deeper than what we can see. Although the skin might be red, a bunion actually reflects a change in the anatomy of the foot. Bunions happen over time. What begins as the big toe pointing toward the second toe ends up as changes in the actual alignment of the bones in the foot. There is also a condition called tailor?s bunion or bunionette. This type of bump differs from a bunion in terms of the location. A tailor?s bunion is found near the base of the little toe on the outside of the foot.
People think of a bunion as being as a bump on the side of the foot near the big toe. However, bunions go deeper than what we can see. Although the skin might be red, a bunion actually reflects a change in the anatomy of the foot. Bunions happen over time. What begins as the big toe pointing toward the second toe ends up as changes in the actual alignment of the bones in the foot. There is also a condition called tailor?s bunion or bunionette. This type of bump differs from a bunion in terms of the location. A tailor?s bunion is found near the base of the little toe on the outside of the foot.
Causes
The main cause of bunions is a mechanical imbalance in the feet which is usually inherited. The mechanical imbalance is known as overpronation, where the feet roll in towards the arch and big toe. This added weight and stress transfer towards the big toe, causes instability in the structures of this area and a bunion develops.
Symptoms
Symptoms, which occur at the site of the bunion, may include pain or soreness, inflammation and redness, a burning sensation, possible numbness. Symptoms occur most often when wearing shoes that crowd the toes, such as shoes with a tight toe box or high heels. This may explain why women are more likely to have symptoms than men. In addition, spending long periods of time on your feet can aggravate the symptoms of bunions.
Diagnosis
A doctor can very often diagnose a bunion by looking at it. A foot x-ray can show an abnormal angle between the big toe and the foot. In some cases, arthritis may also be seen.
Non Surgical Treatment
Long-term treatment of bunions must be directed towards re-balancing the foot, so that we no longer walk with our weight forced on to the inner border of the foot. This is accomplished by controlling and reducing pronation with the use of a high quality arch support or custom made orthotics. These devices comfortably re-balance the feet and overcome pronation. This reduces the abnormal weight forces on the big toe and its metatarsal head, allowing the feet to function normally. As a result, the deformity should not worsen, and the pain should gradually subside. If the foot is not re-balanced, the deformity and pain will become worse.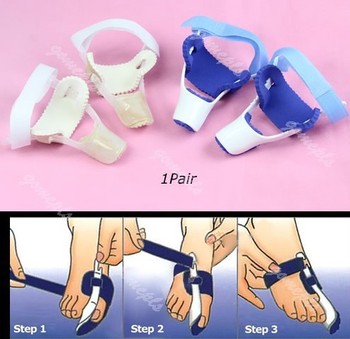
Surgical Treatment
Surgical options, such as a bunionectomy, can remove the bunion and realign the toe. There are several types of surgeries to fix the bunion. The type of bunion you have along with other factors such as the degree of severity and underlying cause of the bunion will determine which approach would be most beneficial for you.
Prevention
Choosing footwear that fits correctly, especially low heeled shoes with plenty of space for the toes, is one of the main ways that bunions can be prevented. Always stand when trying on shoes to ensure they still fit comfortably when the foot expands under your body weight. Try shoes on both feet, and select the size appropriate for your larger foot. Use an extra insole if one shoe is looser than the other. Do not cramp the larger foot. People prone to flat-footedness should consider the use of arch supports, orthotic shoe inserts or special orthotic shoes to prevent or delay the development of bunions.
 People think of a bunion as being as a bump on the side of the foot near the big toe. However, bunions go deeper than what we can see. Although the skin might be red, a bunion actually reflects a change in the anatomy of the foot. Bunions happen over time. What begins as the big toe pointing toward the second toe ends up as changes in the actual alignment of the bones in the foot. There is also a condition called tailor?s bunion or bunionette. This type of bump differs from a bunion in terms of the location. A tailor?s bunion is found near the base of the little toe on the outside of the foot.
People think of a bunion as being as a bump on the side of the foot near the big toe. However, bunions go deeper than what we can see. Although the skin might be red, a bunion actually reflects a change in the anatomy of the foot. Bunions happen over time. What begins as the big toe pointing toward the second toe ends up as changes in the actual alignment of the bones in the foot. There is also a condition called tailor?s bunion or bunionette. This type of bump differs from a bunion in terms of the location. A tailor?s bunion is found near the base of the little toe on the outside of the foot.Causes
The main cause of bunions is a mechanical imbalance in the feet which is usually inherited. The mechanical imbalance is known as overpronation, where the feet roll in towards the arch and big toe. This added weight and stress transfer towards the big toe, causes instability in the structures of this area and a bunion develops.
Symptoms
Symptoms, which occur at the site of the bunion, may include pain or soreness, inflammation and redness, a burning sensation, possible numbness. Symptoms occur most often when wearing shoes that crowd the toes, such as shoes with a tight toe box or high heels. This may explain why women are more likely to have symptoms than men. In addition, spending long periods of time on your feet can aggravate the symptoms of bunions.
Diagnosis
A doctor can very often diagnose a bunion by looking at it. A foot x-ray can show an abnormal angle between the big toe and the foot. In some cases, arthritis may also be seen.
Non Surgical Treatment
Long-term treatment of bunions must be directed towards re-balancing the foot, so that we no longer walk with our weight forced on to the inner border of the foot. This is accomplished by controlling and reducing pronation with the use of a high quality arch support or custom made orthotics. These devices comfortably re-balance the feet and overcome pronation. This reduces the abnormal weight forces on the big toe and its metatarsal head, allowing the feet to function normally. As a result, the deformity should not worsen, and the pain should gradually subside. If the foot is not re-balanced, the deformity and pain will become worse.

Surgical Treatment
Surgical options, such as a bunionectomy, can remove the bunion and realign the toe. There are several types of surgeries to fix the bunion. The type of bunion you have along with other factors such as the degree of severity and underlying cause of the bunion will determine which approach would be most beneficial for you.
Prevention
Choosing footwear that fits correctly, especially low heeled shoes with plenty of space for the toes, is one of the main ways that bunions can be prevented. Always stand when trying on shoes to ensure they still fit comfortably when the foot expands under your body weight. Try shoes on both feet, and select the size appropriate for your larger foot. Use an extra insole if one shoe is looser than the other. Do not cramp the larger foot. People prone to flat-footedness should consider the use of arch supports, orthotic shoe inserts or special orthotic shoes to prevent or delay the development of bunions.
